Sauvignon Blanc Clonal Investigation (2016)
Submitted by Emily Pelton
Veritas Vineyards and Winery
Summary
This study examines the clonal differences between Sauvignon Blanc FPS 1, FPS 18, ENTAV 376, and ENTAV 241 planted in the same year in the same vineyard block. Grapes were harvested and pressed on the same day but kept separate, and all treatments between lots were kept the same. Yields were different between some clones, and the FPS clones tended to have higher malic acid and YAN. Clone 241 tended to have lower acidity and higher pH than the other clones, and the opposite trend was observed for FPS 1. Wines produced from FPS 1 and ENTAV 376 had the highest levels of 3-MH. Descriptive analysis found several differences between clones. Wine made with ENTAV 376 was highest in most sensory descriptors, and most people preferred Clone 376. However, these differences may not all be clonal, but could be due to variations between fermentations. As such, this study should be repeated in order to determine if clone 376 is truly much more aromatically intense.
Introduction
Clonal evaluation is an important process in determining whether particular clones are best suited for particular vineyards sites. Clones can vary widely not only in sensory characteristics in finished wine, but also in vine vigor, cluster architecture, and yield. These can have tremendous impacts on ripening, vineyard management, and disease pressure. As a result, ongoing research must be implemented on different clones to determine which appellations and wine styles they are most suited for. This study examines the clonal differences between Sauvignon Blanc FPS 1, FPS 18, ENTAV 376, and ENTAV 241 planted in the same year in the same vineyard block.
Results and Discussion
Yields were different between some clones, and the FPS clones tended to have higher malic acid and YAN. Clone 241 tended to have lower acidity and higher pH than the other clones, and the opposite trend was observed for FPS 1. Wines produced from FPS 1 and ENTAV 376 had the highest levels of 3-MH.
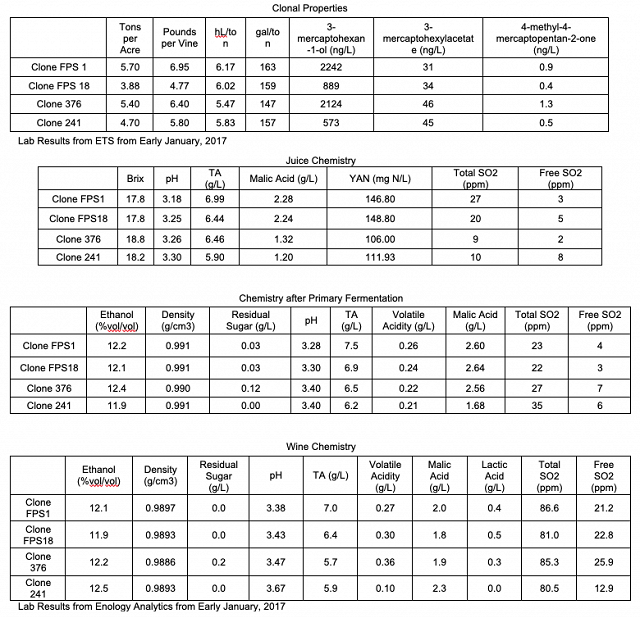
For the January 25 tasting, descriptive analysis found strong trends for the following attributes: Tropical Fruit, Varietal Character, Overall Aromatic Intensity, and Body. The LSD values for Tropical Fruit, Varietal Character, Overall Aromatic Intensity, and Body are: 1.16, 1.13, 1.09, and 0.84, respectively.
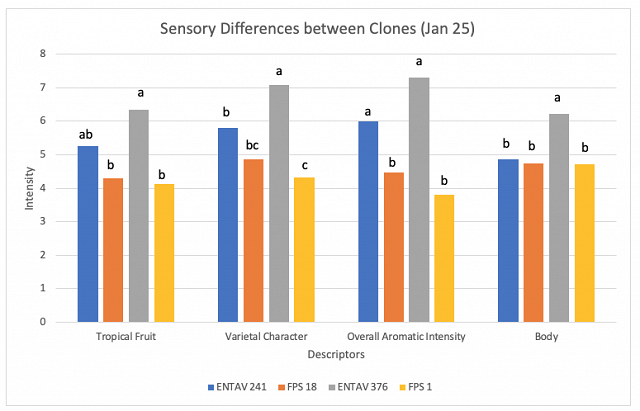
For the Jan 25 tasting, in general people tended to prefer Clone 376, with Clone 241 being the second most preferred, FPS 18 being the third-most preferred, and FPS 1 being the least preferred. Many people, however, did not prefer Clone 241, either. Clone 376 was often described as having the most Varietal Character, Tropical Fruit, and Overall Aromatic Intensity (significantly higher in this wine), as well as being the most lush wine. This corresponds to the high levels of 3-MH found in this clone. Clone FPS 1, however, also had high levels of 3-MH yet did not show high for these characteristics. Some people thought the FPS 1 tasted oxidized and musky, whereas another person thought that 241 was oxidized.
For the February 15 tasting, a strong trend was found for Minerality for Clone FPS 18 to have lower minerality than Clone FPS 1. In general, there was a slight trend for Clone 376 to have higher overall ratings for all descriptors except for Herbaceous/Green.
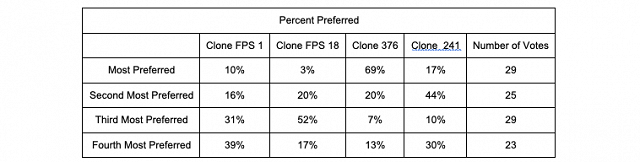
On February 15 people tended to prefer Clone 376, and the least preferred clones were Clone 241 and Clone FPS 1. However, each ranking only received 10 votes, so these results are not very strong. Clone 376 was described as having brighter aromatics, being explosive, having higher thiols and classic Sauvignon Blanc notes. FPS 1 was described as being flat aromatically.
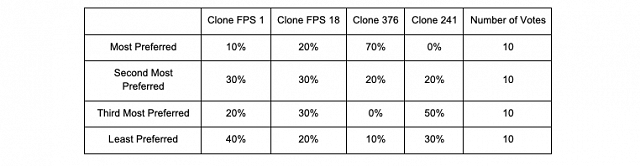
For the April 12 Tasting, there was a strong trend for Clone 376 to have higher Overall Aromatic Intensity than the other two wines. It also tended to have higher scores for Body, Tropical Fruit, and Varietal Character. In general, people tended to prefer ENTAV 376 at the April 12 tasting.
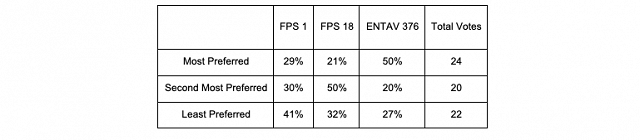
In conclusion, descriptive analysis found all four clones to be very different. Wine made with ENTAV 376 was highest in most sensory descriptors, and wine made from FPS 1 and FPS 18 were lower in these descriptors. In general, most people preferred Clone 376. However, these differences may not all be clonal, but could be due to variations between fermentations. As such, this study should be repeated in order to determine if clone 376 is truly much more aromatically intense.
Methods
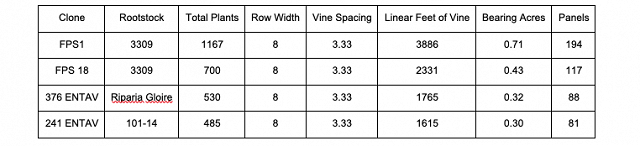
Four Sauvignon Blanc Clones were planted in the same vineyard block (Toby’s Vineyard) in 2012 with the following characteristics:
These were harvested on 8/24 and were pressed separately on the Champagne press cycle on Europress, with the press fraction extracted at step 21. 50ppm sulfur dioxide was added to the press tray. On 8/26, Cinn Free was added at 1.6mL/hL and juice was cold settled at 45F. Juice was racked separately on 8/28 into stainless steel barrels, and on 8/29 20g/hL Elixir Yeast (rehydrated with 25g/hL Go Ferm) was added. On 9/3 all four fermenting musts were adjusted with 35g/hL Fermoplus DAP Free. On 9/12 primary fermentation was complete. 35ppm sulfur dioxide was added on 10/2 to stabilize the wine, and another 13ppm was added on 10/22. Batonnage was performed twice per week for one month (11/2, 11/7, 11/10, 11/15, 11/18, 11/22, 11/25, 11/28, 12/1), then samples were taken.
This project was tasted on January 25, February 15, and April 12. The sensory data for the January 25 tasting session had to be manipulated to achieve a balanced data set. Judges who had not completed rating wines for certain descriptors were removed from consideration for descriptive analysis. In order to balance the number of judges in each group as a result of this, 1 judge had to be moved from group 2 to group 3, and 2 judges had to then be eliminated from group 2. The resulting statistical set-up considered groups of judges as judges, and replications were the different judges within a group. There were three groups total, each with 8 judges. Data was analyzed using Panel Check V 1.4.2. Because this is not a truly statistical set-up, any results which are found to be statistically significant (p<0.05) will be denoted as a “strong trend” or a “strong tendency,” as opposed to general trends or tendencies. The statistical significance here will ignore any other significant effects or interactions which may confound the results (such as a statistically significant interaction of Judge x Wine confounding a significant result from Wine alone). The descriptors used in this study were Tropical Fruit, Herbaceous/Green, Varietal Character, Minerality, Overall Aromatic Intensity, and Body.
For the February 15 tasting, the same procedures for data analysis were followed. One judge was eliminated from Group 1 and Group 2 in order to balance the data set for descriptive analysis. This resulted in a total of 3 judges per group, for 9 judges overall. For the April 12 tasting, the same procedures for data analysis were followed. Additionally, Clone 241 was not tasted due to concerns about oxidation. In order to balance the data set for descriptive analysis, 2 judges were moved from group 2 to group 3, and one further judge was eliminated from group 2. This resulted in a final data set of 3 groups each with 6 judges.
